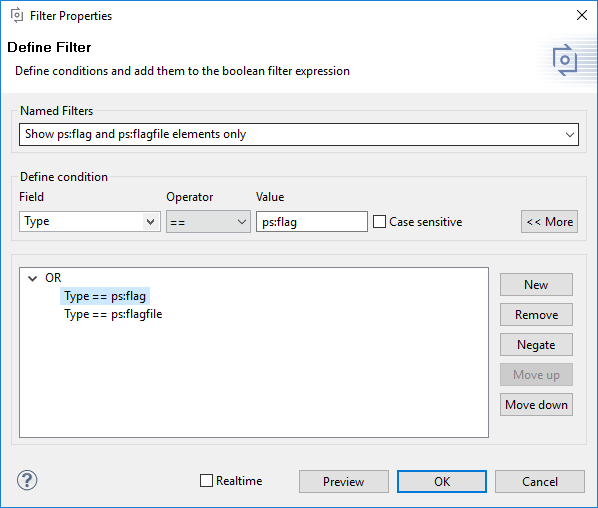
Most views and editors support filtering. Depending on the type of view, the filtered elements are either not shown (table like views) or shown in a different style (tree views). Filters can be defined, or cleared, from the context menu of the respective view/editor page. When the view/editor has several pages the filter is active for all pages.
Arbitrarily complex filters based on comparison operations between feature/element properties (name, attribute values, etc.) and logical expressions (and/or/not) are supported. Comparison operations include conditions like equality and containment, regular expressions (matches) and checks for the existence of an attribute for a given element (empty/not empty). See Section 9.10, “ Regular Expressions ” for more information on regular expressions.
Filters can be named for later reuse using the Named Filter field. The drop-down box allows access to previously defined filters. Fast access to named filters is provided by the Visualization view, which can be activated using the Windows->Views->Other->Variant Management->Visualization item. See Section 7.4.2, “ Visualization View ” for more information on the view.